
Smart NOTAMs for flight crew briefings
The center of gravity (CG) plays a key role in flight safety and efficiency. Pilots and flight planners rely on accurate CG calculations to ensure that an aircraft operates within its safe envelope limitations.
In this blog, we’ll go through the basics of CG and a step-by-step of how to calculate center of gravity.
Or, you can bypass the complications and head straight to our streamlined Weight & Balance module.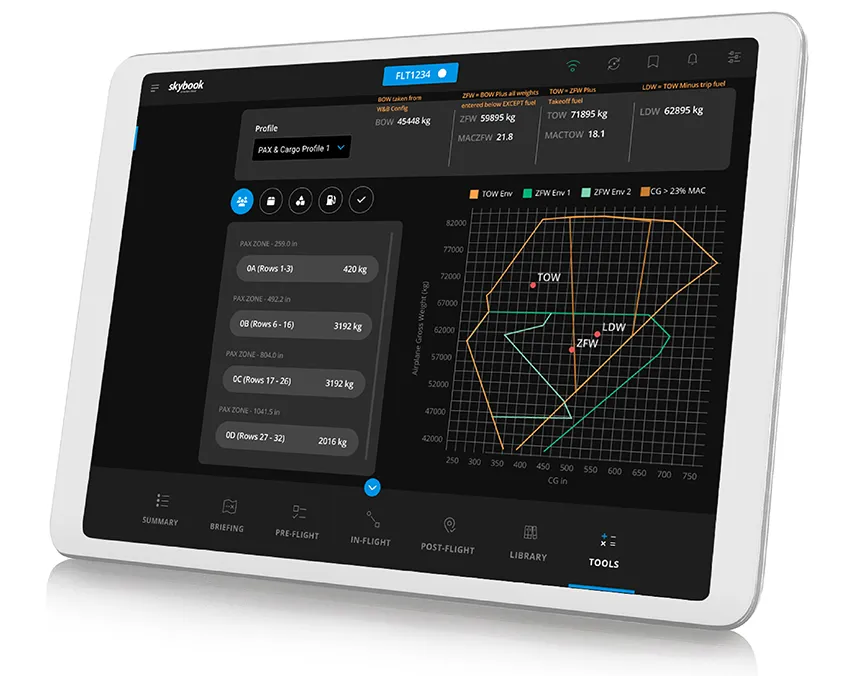
The center of gravity is the exact point where the aircraft's total weight is considered to be concentrated.
An accurate CG calculation ensures the aircraft is correctly balanced and provides safe controllability. If the CG is too far forward or aft, the aircraft could become difficult to control, leading to unsafe flying conditions for the flight crew.
Learn more about the importance of weight & balance and center of gravity.
CG is commonly calculated by dividing the total moment (the force of weight at a distance) by the total weight of the aircraft.
The formula is: CG=Total Moment /Total Weight
1 - Collate Data for:
Aircraft Empty Weight & CG: Obtain the aircraft's empty weight and its CG location from the aircraft's specific weight and balance configuration.
Weight of Passengers, Cargo, and Fuel: Determine the weight and location of all items being loaded on the aircraft.
2 - Calculate Moments:
For each weight (passengers, cargo, fuel, etc), multiply the weight by the distance from the datum to find the moment. Moment=Weight×Arm (Distance)
3- Sum the Moments & Total Weight:
Add up all the moments and the total weight to find the overall moment and total weight of the loaded aircraft.
4 - Apply the Formula:
Divide the total moment by the total weight to find the CG location. CG=Total Moment/Total Weight
5 - Check the CG Limits:
Compare the calculated CG with the aircraft’s allowable CG flight envelope range from the flight manual to ensure it’s within the safe operating limits.
These days, many weight calculations, like the basic operating weight, can be pre-configured and automatically integrated into the weight & balance section of an EFB app.
Aircraft Load:
Step 1: Calculate Moment for Each Component
To find the moment, multiply the weight by the arm for each component:
Step 2: Calculate the Total Weight & Total Moment
Step 3: Calculate the Center of Gravity (CG)
Divide the total moment by the total weight to find the CG:
The aircraft’s center of gravity is located 286.5 inches from the reference point. This CG must fall within the aircraft's safe operational limits to ensure stable flight.
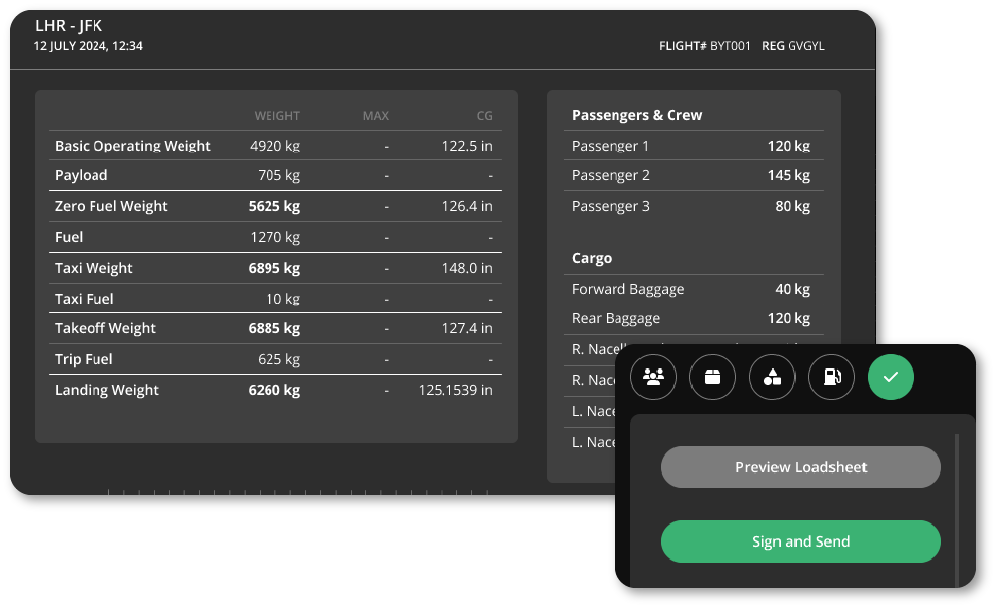
Understanding and accurately calculating the center of gravity is essential for ensuring smooth and safe flight operations.
With modern tools like electronic flight bags (EFBs), pilots can access weight and balance data to perform these calculations more efficiently and accurately.
The W&B loadsheet data can then be signed off and synced to the ground system for secure data storage and providing flight summary reports. This also ensures a robust audit trail and provides extra safety checks if necessary.
Why not read more about how the EFB weight & balance calculator can save time for the flight crew.